Please Sign in to view recently saved searches.
1. Geographic and Economic Overview
Cameroon is located in Central Africa, with its southwestern border along the Gulf of Guinea. It shares land borders with Nigeria to the northwest, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, the Republic of the Congo to the southeast, and Gabon and Equatorial Guinea to the south. Benefiting from a favorable geographical position and rich natural conditions, Cameroon is often referred to as "Miniature Africa" due to its diverse landscape and ecosystems. The country is endowed with abundant natural resources and holds significant potential in agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, fisheries, and mineral exploitation. It also possesses a certain level of industrial foundation.
In 2023, Cameroon's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) reached approximately USD 47.95 billion, marking a year-on-year growth of 4.0%. The per capita GDP increased to USD 1,673. Within the Central African Economic and Monetary Community (CEMAC), Cameroon accounts for as much as 45% of the region's total economic output.
2. Regional and International Role
As a founding member of the African Union, Cameroon plays a pivotal role in the political and economic landscape of Sub-Saharan and Central Africa. CEMAC comprises six member states: Cameroon, the Central African Republic, the Republic of the Congo, Gabon, Equatorial Guinea, and Chad. Among these, Cameroon is the most populous and the largest economy, serving as a key trade hub within the region. According to the World Bank and other international organizations, Cameroon's economic output accounts for nearly 50% of the CEMAC total.
Cameroon maintains broad cooperation with global institutions such as the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund, and the World Trade Organization. As a member of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie, the Commonwealth, and the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, Cameroon enjoys long-standing ties with European countries such as the UK and France, as well as with many Islamic nations.
3. Key Industries
3.1 Mineral Resources
Cameroon is rich in mineral resources. Major proven reserves include:
- Iron ore: 6.6 to 8.6 billion tonnes
- Bauxite: Approx. 1.1 billion tonnes
- Rutile: Approx. 3 million tonnes
- Uranium: Approx. 20,000 tonnes
Other minerals such as tin, nickel, cobalt, diamonds, gold, marble, limestone, and mica are also present. Except for diamonds and gold, most deposits remain in the exploration or pre-development phase.
Oil and Natural Gas: Cameroon holds an estimated 100 million tonnes of oil and 500 billion cubic meters of natural gas. Crude oil production declined to 23.88 million barrels in 2023, a 6.7% drop year-on-year. Natural gas output reached 2.28 billion cubic meters in the same year.
Other Minerals: Key iron ore deposits include the Mbalam mine in the East Region (approx. 4 billion tonnes), the Mamelles mine in the South (approx. 632 million tonnes), and the Nkout deposit (approx. 2–4 billion tonnes). All are currently undeveloped. Cameroon also ranks second in Africa for bauxite reserves, located primarily in Minim-Martap and Ngaoundal in the Adamawa Region, and Fongo Tongo in the West Region.
3.2 Forest Resources
Cameroon has abundant forest coverage, totaling 22.5 million hectares, which is 46.3% of its land area and 11.95% of global tropical forest coverage. Of this, 16.9 million hectares are classified as exploitable, with a timber volume of 4 billion cubic meters. Timber and wood products are Cameroon's second-largest export commodity after petroleum, contributing roughly 14% to total exports.
3.3 Agriculture
With ample sunshine, abundant rainfall, and low incidence of natural disasters, Cameroon enjoys favorable conditions for agricultural development and is a leading agricultural producer in Central Africa. Agriculture accounts for a significant portion of national economic output. The sector - including farming, forestry, livestock, and fisheries - employs around 60% of the workforce and is a cornerstone of national poverty alleviation. About 90% of rural households are engaged in farming, and one-third rely on agricultural exports for their livelihood. Cameroon's main export crops include cocoa, coffee, natural rubber, cotton, bananas, and palm oil.
3.4 Forestry
Cameroon's forest area is approximately 22.5 million hectares, second only to the Democratic Republic of the Congo in Africa, accounting for 46% of its national territory. Forests are primarily located in the East, South, and Central regions. About 17.5 million hectares are commercially exploitable, with timber reserves of 4 billion cubic meters. Forestry is a pillar of the national economy, contributing around 2% to GDP. Timber is the third-largest export after oil and cocoa, mainly exported as logs and sawn wood. In 2022, the forestry sector grew by 4.8% thanks to rising exports and expansion of domestic wood processing.
3.5 Industry
Cameroon's industrial sector has developed a foundational scale and ranks among the more advanced in Sub-Saharan Africa. It is concentrated in mining, energy, resource processing, agro-processing, food processing, and consumer goods manufacturing. However, production in areas such as machinery, vehicles, tractors, instruments, home appliances, and other manufacturing sectors remains limited or non-existent, resulting in heavy dependence on imports.
4. Economic and Trade Cooperation
4.1 Multilateral and Regional Economic Cooperation
Cameroon is an active member of CEMAC and the Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS), promoting multilateral cooperation in trade, finance, transportation, and labor mobility. The country is committed to advancing regional integration for shared growth and prosperity.
4.2 Preferential Trade Arrangements
In November 2023, Cameroon signed the Samoa Agreement with the European Union, replacing the Cotonou Agreement signed in 2000.
4.3 CEMAC Trade Benefits
As a CEMAC member, Cameroon participates in a unified external tariff regime. Enterprises based in the CEMAC or ECCAS regions that source more than 40% of their raw materials locally are eligible to apply for a special license. This license allows for duty-free exports within the two communities.
4.4 Free Trade Agreements
In March 2018, Cameroon joined 43 other African nations in signing the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) agreement in Rwanda. The agreement took effect on May 30, 2019, and Cameroon ratified it on October 31, 2019. The AfCFTA is the world's largest free trade area by membership since the establishment of the WTO, covering a market of 1.2 billion people and USD 3 trillion. In July 2022, Cameroon was selected among seven countries to pilot free trade implementation under the AfCFTA framework.
5. Foreign Trade
According to Cameroon's National Institute of Statistics, the total value of merchandise exports in 2023 was XAF 2.99 trillion, representing a 14.2% decline year-on-year. Key figures include:
- Crude oil exports: 3.084 million tonnes (–13.6%), XAF 1.1271 trillion (–25.6%)
- Liquefied natural gas exports: 1.373 million tonnes (+1.8%), XAF 421.4 billion (–33.3%)
- Timber and wood products: 1.365 million cubic meters (–21.1%), XAF 288.3 billion (–8.4%)
- Cocoa beans: 180,000 tonnes (–23.5%), XAF 359.1 billion (+12.9%)
Total imports were XAF 4.99 trillion, up 1.7% year-on-year, resulting in a trade deficit of XAF 2.00 trillion, a 40.3% increase from the previous year.
5.1 Trade Composition
The top five exports in 2023 were:
- Crude oil (37.7% of total exports)
- Liquefied natural gas (14.1%)
- Cocoa beans (12.0%)
- Timber (9.6%)
- Raw cotton (4.9%)
The top imports were:
- Hydrocarbons (24.2% of total imports)
- Machinery and electrical equipment (13.1%)
- Chemicals (10.7%)
- Cereals (7.8%)
- Frozen fish (3.7%)
5.2 Major Trade Partners
In 2023, Cameroon's top five export destinations accounted for 62.3% of total exports:
- Netherlands (23.2%)
- France (12.3%)
- India (9.6%)
- China (7.8%)
- Chad (5.0%)
- Italy (4.4%)
Top 10 import sources accounted for 59.6% of total imports, led by:
- China (19.0%)
- India (11.6%)
- France (7.6%)
- USA (4.8%)
- Belgium (4.4%)
6. China–Cameroon Trade
According to China Customs data, bilateral trade between China and Cameroon reached USD 4.23 billion in 2023, up 13.4% year-on-year. Chinese exports to Cameroon stood at USD 3.71 billion, a 20.8% increase, while imports from Cameroon dropped by 21.2% to USD 520 million.
6.1 Trade Structure
China's exports to Cameroon mainly consist of:
- Mechanical and electrical products
- High-tech goods
- Footwear
- Textile yarns, fabrics, and related products
- Steel
- Apparel and accessories
- Agricultural products
- Cement and clinker
- Auto parts and vehicles
According to Cameroonian data, exports to China primarily include crude oil, liquefied natural gas, and timber.
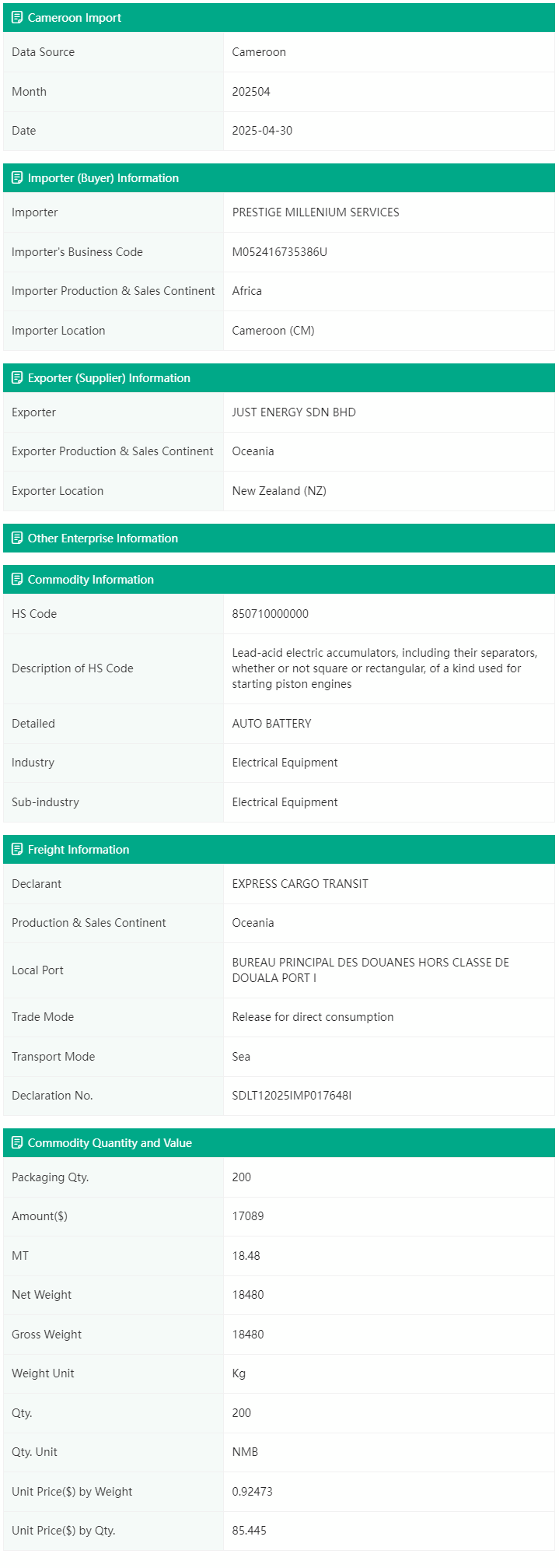
7. Blooming Trade Data for Cameroon
Blooming provides high-quality, continuously updated import and export customs data for Cameroon. The dataset includes vital information on importers, exporters, traded products, logistics and transport details, as well as full transaction volumes, values, and pricing. These insights enable traders to accurately gauge market prices, identify potential clients and reliable suppliers, and seize commercial opportunities - even amid global trade tensions - to maintain a competitive edge.
Do you want to understand the market demand in Cameroon? Are you looking to expand your international market presence in Cameroon? Are you seeking more cooperation with clients and reliable suppliers in Cameroon?

Sample Data